Flutter是基于Dart语言,而Dart是单线程语言,通常情况下,任务都在主线程(这里的主线程不同于Native的主线程)里面执行
事件循环(event loop)
和iOS的Runloop类似,Dart中的线程也使用事件循环和消息队列的方式执行任务,在Dart中,线程叫做isolate,而这个更像是进程的概念(不同的isolate不共享状态,不存在锁的问题,并且通过port进行通信)
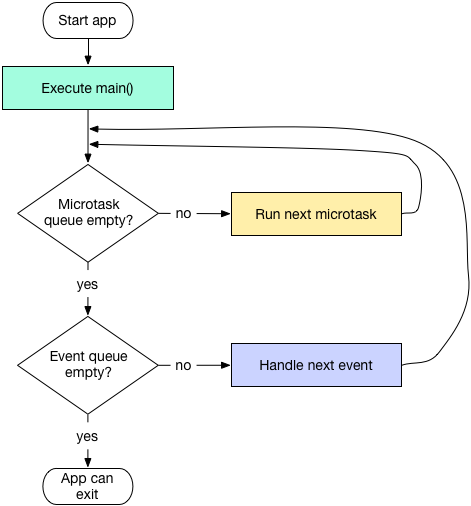
应用程序启动后,执行main函数,然后会开始运行main isolate,每个isolate都有两个事件队列,分别是event queue和microtask queue,有点类似iOS中的sourcd0, source1,micro queue优先级高于event queue,只有microtask queu为空时,才会执行event queue
event queue: 负责处理I/O事件,手势,Timer,绘制,其他外部事件(如通过Future添加的事件)microtask queue: 负责处理优先级更高的事件
由于microtask queue会优先执行,为了避免渲染,和手势处理的延迟,对于复杂的计算,不应该放在microtask queue里面,应该放到event queue,而对于相对比较耗时的计算,应该考虑放到其他isolate运行(多线程),避免界面卡顿
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| void testFuture() async {
Future((){
print("Future event 1");
});
Future.sync(() {
print("Future sync microtask event 2");
});
Future.microtask((){
print("microtask event");
});
}
testFuture();
print("testFuture()执行完了");
|
上面代码输出
1
2
3
4
| Future sync microtask event 2
testFuture()执行完了
microtask event
Future event 1
|
Future
await, async
await和async用于等待Future完成,并且不会阻塞当前执行
await: 作用于Future对象,用于异步等待Future<T>完成,并且返回Tasync: 作用于方法,与await配合使用,用于声明方法需要等待
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| Future<String> dataReqeust() {
return Future<String>(() {
print("request begin");
print("request end");
return "data";
});
}
Future<String> loadData() async {
var data = await dataReqeust();
return data;
}
void main() async {
var data = await loadData();
print(data);
print("testFuture()执行完了");
}
|
输出
1
2
3
4
| request begin
request end
data
testFuture()执行完了
|
由于Dart是单线程的,如果创建一个耗时的Future,则可能会导致后面的任务延后执行
async和await的本质是协程(coroutine)的语法糖,协程可以让单线程支持异步调度的,减少进程调度带来的开销
then, catchError, whenComplete
then: 在Future执行完成后立即调用catchError: 在Future执行过程中,出现异常时调用(throw error)whenComplete: 当Future完成(包括抛出异常)都会走到这个方法
上面三个方法都会返回一个Future,Dart会把任务放到回调队列里面,返回值又可以视为一个新的Future
当调用上面三个方法,这时候Dart会把方法注册到zone中的回调方法里面,而如果这时候Future已经执行完了,那么方法会被放到microtask queu里面)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| void testFuture() async {
Future x1 = Future(() {
return 10;
});
x1.then((value) {
print('2');
}).then((v) {
print('3');
}).catchError((e) {
print("4");
}).whenComplete((){
print("5");
}).then((v) {
print('6');
throw "error2";
}).catchError((e) {
print("7");
});
print('1');
}
void main() {
testFuture();
print("testFuture()执行完了");
}
|
输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| 1
testFuture()执行完了
2
3
5
6
7
|
结合microtask queue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| void testFuture() async {
Future x1 = Future(() => null);
x1.then((value) {
print('6');
Future.microtask(() => print('7'));
}).then((value) => print('8'));
Future x = Future(() => print('1'));
x.then((value) {
print('4');
Future(() => print('9'));
}).then((value) => print('10'));
Future(() => print('2'));
Future.microtask(() => print('3'));
print('5');
}
testFuture();
print("testFuture()执行完了");
|
输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| 5
testFuture()执行完了
3
6
8
7
1
4
10
2
9
|
Isolate
Isolate是dart的进程模型,有独立的存储空间,独立的运行环境,不像线程可以直接共享内存状态,基于port通信,除了main isolate,其他isolate不支持UI相关的操作,通常用于计算密集型的任务,这里说的进程指的是在Dart环境下的进程,不是平台的进程,从平台的角度来看还是线程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| import 'dart:isolate';
void func(List<dynamic> argument) {
SendPort send = argument[0];
int value = argument[1];
print('进入子进程任务!!,收到参数 $value');
send.send(1000);
}
void testIsolate() async {
ReceivePort port = ReceivePort();
int value = 10;
Isolate iso = await Isolate.spawn(func, [port.sendPort, value]);
port.listen((message) {
print("收到子进程的消息:$message");
port.close();
iso.kill();
});
}
void main() {
testIsolate();
}
|
dart提供了一个方法compute封装了一个方法,可以使用Future很方便的执行,内部是对isolate的封装
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| import 'package:flutter/foundation.dart';
int func2(int v) {
print("子进程收到参数:$v");
print("子进程执行耗时操作");
var sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 9999999; i++) {
sum = i;
}
return sum;
}
void computeTest() async {
print('外部代码1');
var result = await compute(func2, 10);
print("执行完成:$result");
print('外部代码2');
}
void main() async {
computeTest();
}
|
输出
1
2
3
4
5
| flutter: 外部代码1
flutter: 子进程收到参数:10
flutter: 子进程执行耗时操作
flutter: 执行完成:9999998
flutter: 外部代码2
|
参考链接
