正向开发的时候通常是使用xcode对app进行调试,我们先来看看xcode的调试流程
- 手机启动app进程
- 手机启动
debugservice服务,debugserver附加到App进程 - 调试器
lldb通过连接debugservice进行调试
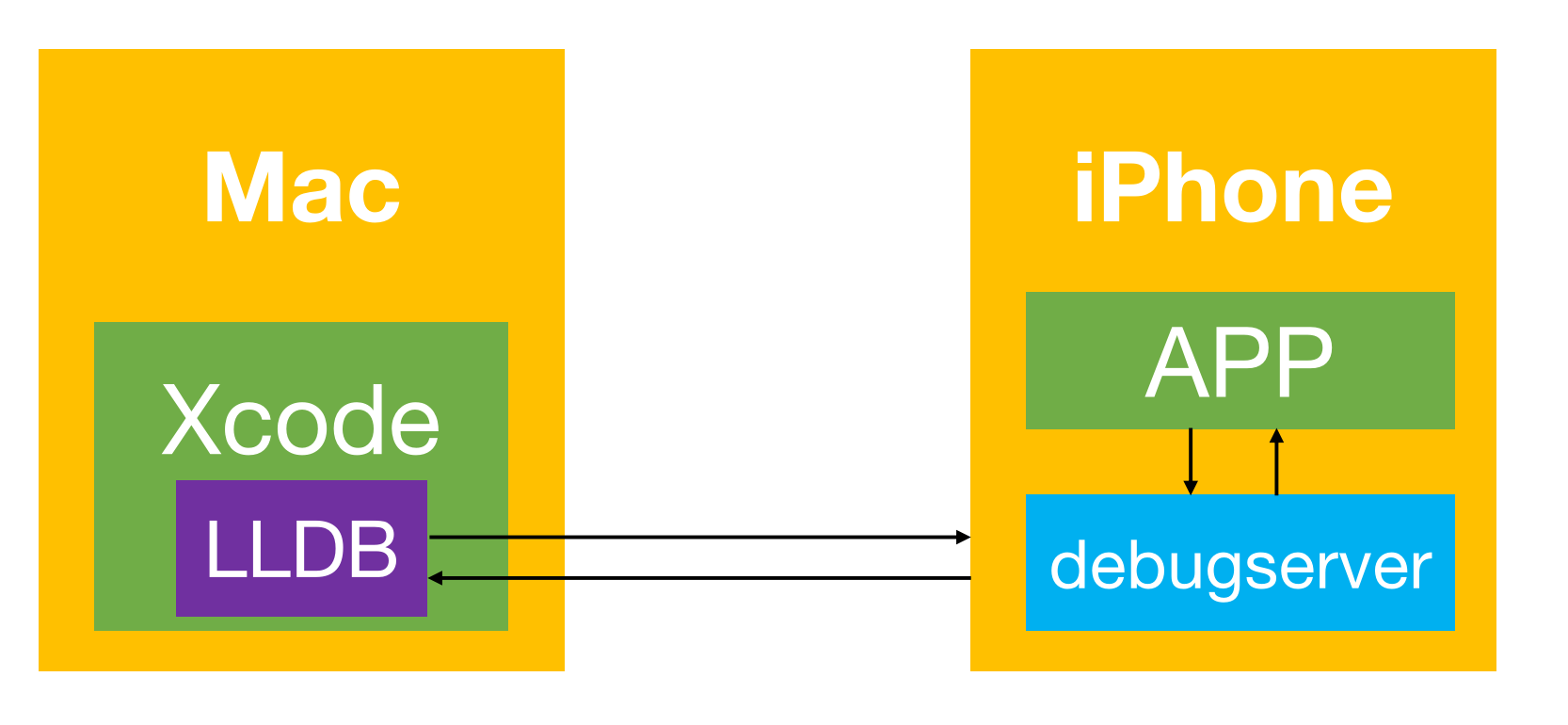
debugservice
Xcode调试用到的debugservice位于/Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/iPhoneOS.platform/DeviceSupport/13.2/DeveloperDiskImage.dmg这个dmg下面,打开后可以在usr/bin/debugserver找到
当手机第一次通过xcode调试时,会把该文件拷贝到手机/Developer/usr/bin/debugserver下,未使用xcode调试过的手机没有该文件,这个程序只能调试通过xcode安装的app,无法调试从商店下载的app,为了调试其他的App,我们需要修改它的权限,把下面权限签到可执行文件
1 |
|
使用ldid签名
1 | # 安装ldid |
得到新的debugserver,传到手机/user/bin/debugserver上,这样可以直接在命令行使用
1 | scp debugserver root@xx.xx.xx.xx:/user/bin/ |
还需要给debugserver添加可执行权限
1 | chmod +x debugserver |
调试
1. debugserver附加到进程
让debugserver附加到App进程上,指定端口号和进程
1 | debugserver 127.0.0.1:端口号 -a 进程id/进程名称 |
我们如果直接使用xcode自带的debugserver来操作的话,会报下面错误,原因是debugserver权限不足
1 | debugserver-@(#)PROGRAM:LLDB PROJECT:lldb-900.3.98 |
2. debugserver启动调试
如果App没有运行,可以直接启动App调试
1 | # 后面接的是完整路径 |
通过lldb连接调试器
1 | # 进入lldb模式 |
这个时候进程会被暂停,可以使用continue让程序继续走
可能会出现下面问题
1 | (lldb) process connect connect://xx.xx.xx.xx:12121 |
如果出现上面问题,可以通过端口转发到本地,使用USB端口转发速度也会更快,ip换成localhost
1 | iproxy 2333 3333 |
接下来使用lldb命令即可,与xcode调试一样
退出调试
1 | (lldb) exit |
每次连接调试的时候都很麻烦,我们可以通过别名来简化连接,如下
1 | # 使用 con 代替 process connect connect://xx.xx.xx.xx:12121 |
lldb常用命令
- 列出所有断点:
breakpoint list, br li - 打开、关闭某个断点:
breakpoint enable, breakpoint disable, br dis, br del - 打印参数:
frame variable, fr v - 打印方法名和行数:
frame info - 打印寄存器的值:
register read - 修改寄存器的值:
register write rax 123 - 列出文件加载基地址:
image list - 执行地址的加减运算:
p/x
反调试
使用ptrace函数反调试
debugserver之所以可以调试APP, 是依赖一个系统函数ptrace(process trace 进程跟踪). 此函数提供了一个进程监听控制另外一个进程, 并且可以检查被控制进程的内容和寄存器里面的数据. 可以用来实现断电调试和系统调用跟踪. iOS中没有提供此函数的头文件, 但不是私有API.
ptrace函数在iOS项目中不能找到,在MacOS工程可以引用到,我们把需要用到的函数声明搬过来
1 | /** |
找地方执行,可以在load方法
1 | + (void)load { |
使用sysctl函数反调试
使用sysctl函数可以判断当前程序是否正在被调试,需要隔一段时间检测一下
1 |
|
反反调试
上面反调试方法都是C语言的方法,而我们知道fishhook可以 hook C方法,所以上面两个方法可以被fishhook替换掉
这时候我们就需要让系统的C方法不被hook,我们可以在别人hook之前换成我们自己的实现,然后别人再hook的时候就只是hook我们替换过的实现了,如何确保我们的hook在别人之前调用呢
我们知道,dyld加载App的时候,动态库是先加载的,而动态库的加载顺序是根据MachO文件描述的顺序(XCode中编译的顺序一样,也就是Frameworks,Libraries,and Embedded Content配置的顺序),我们可以用一个防护的动态库让我们的动态库先执行
当然如果MachO文件的动态链接库的顺序被改变了,还是会被别人先hook,这个成本就比较高了