我们在开发的过程中,经常会用到系统自带的库,如 Foundation,UIKit 等,这些库存放在什么地方呢,我们可以用 MachOView查看编译好的文件的Load Command看到依赖的动态库的路径
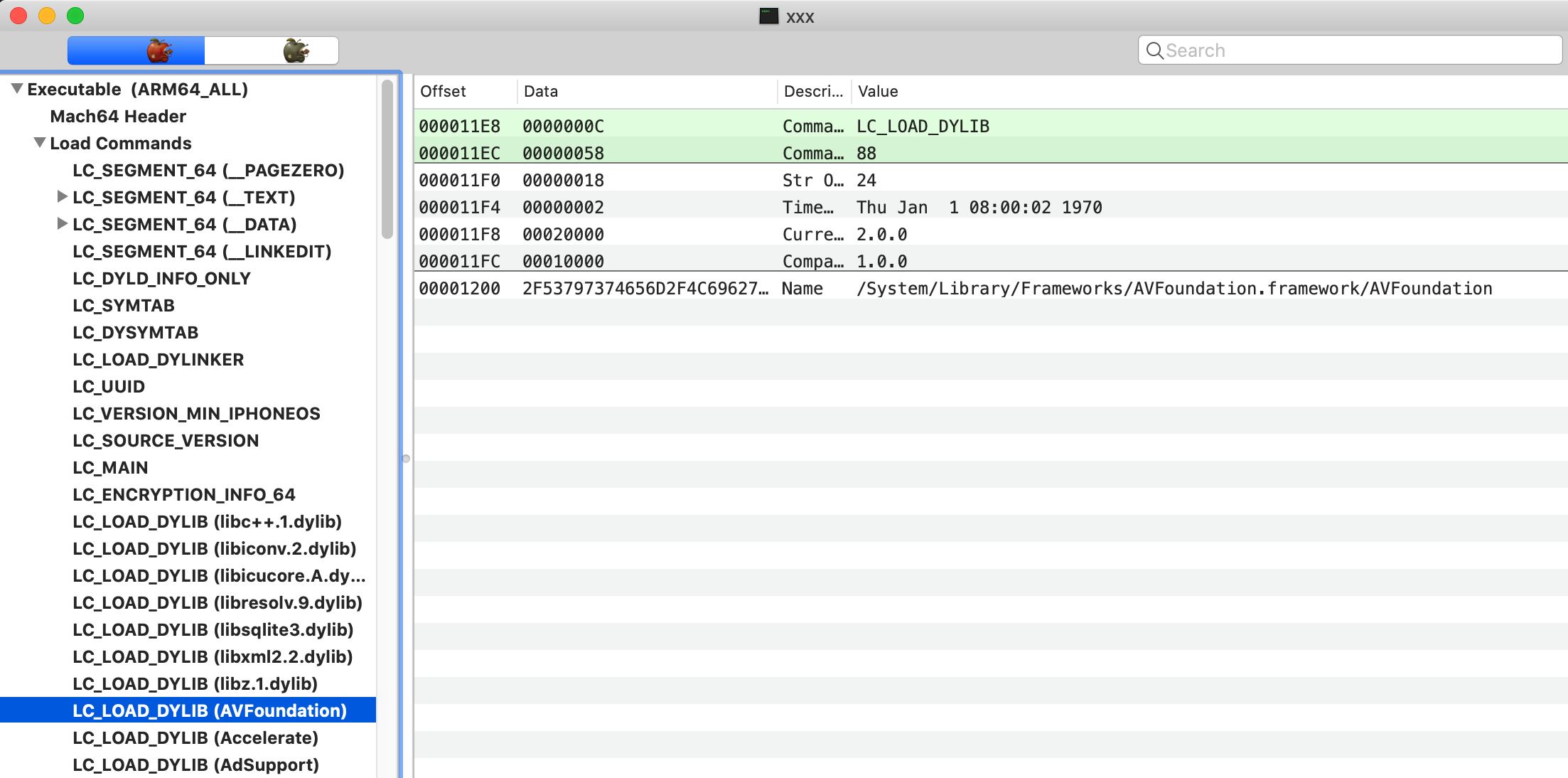
这里可以看到,动态库的路径为/System/Library/Frameworks/AVFoundation.framework/AVFoundation,我们连接到手机查看发现,framework 文件夹存在,但是并没有可执行文件
动态库共享缓存
从iOS 3.1开始,为了提高系统的性能,所有的系统库文件都被打包合并成一个大的缓存文件中,而原来的动态库文件则被去除了,系统直接去缓存文件中加载动态库,该共享缓存文件保存在/System/Library/Caches/com.apple.dyld/目录下
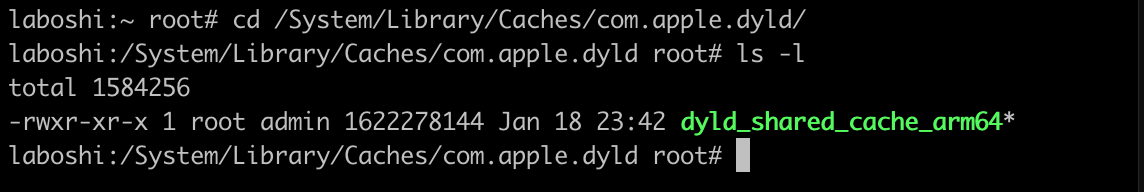
可以看到,该缓存库有1547MB,我们把共享库拷贝到本地
1 | scp root@xx.xx.xx.xx:/System/Library/Caches/com.apple.dyld/dyld_shared_cache_arm64 ~/Desktop/dyld_shared_cache_arm64 |
我们通过工具dsc_extractor把系统库从共享缓存库分离出来,该工具也在dyld项目里面,在该项目中找到/launch-cache/dsc_extractor.cpp文件,我们需要自己编译一下,修改文件,只保留下面代码,其他删除
1 | // #if 0 |
使用clang++编译该源文件
1 | clang++ -o dsc_extractor dsc_extractor.cpp |
编译后得到dsc_extractor,创建文件夹dyld_shared_cache,存放分离出来的动态库
1 | ./dsc_extractor dyld_shared_cache_arm64 dyld_shared_cache |
在dyld_shared_cache/System/Library/Frameworks可以看到动态缓存库中的所有合并的系统库,找到UIKit.framework/UIKit,这个就是真实的UIKit,但是只有8kb
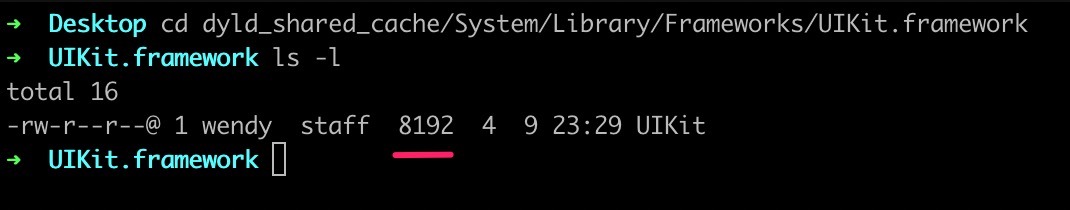
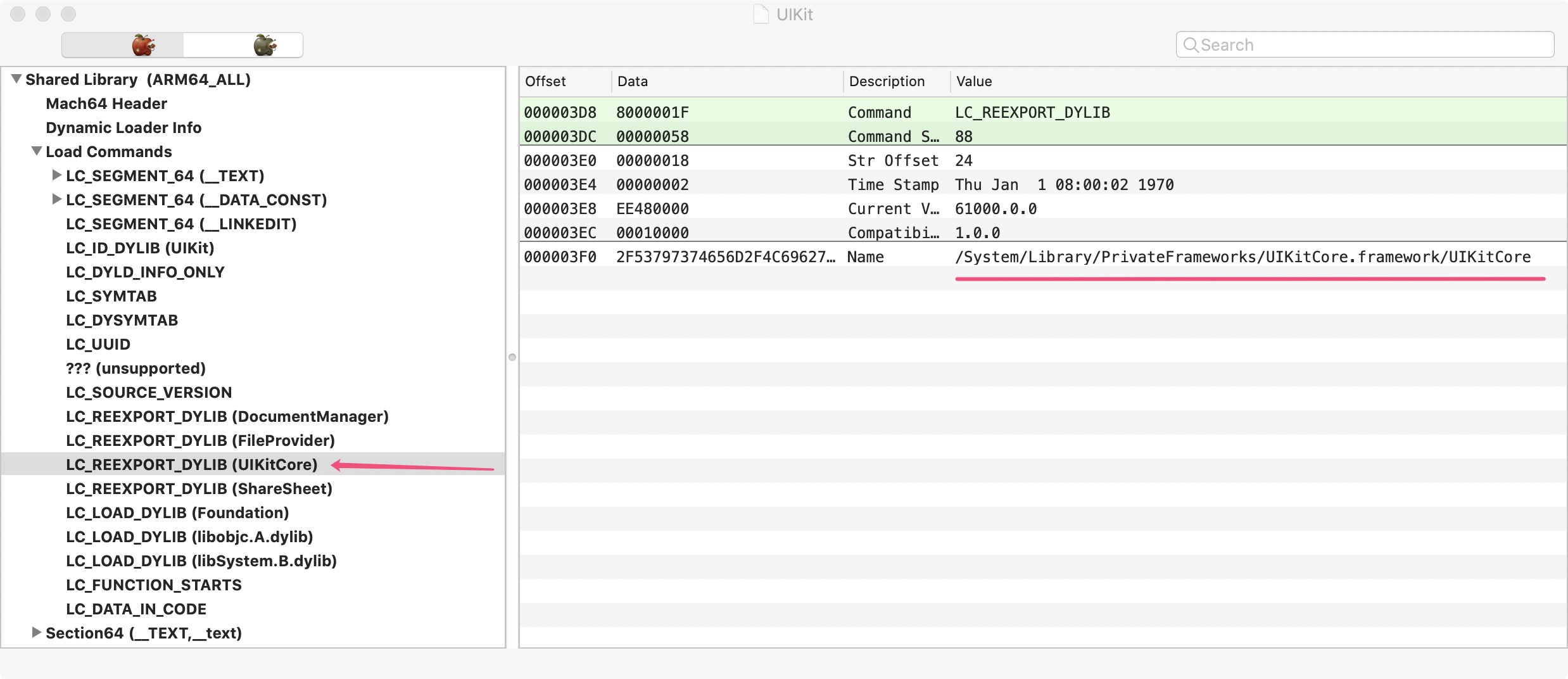
使用MachOView工具查看,可以看到,UIKit引用UIKitCore,核心代码在PrivateFrameworks/UIKitCore.framework/UIKitCore,有30MB
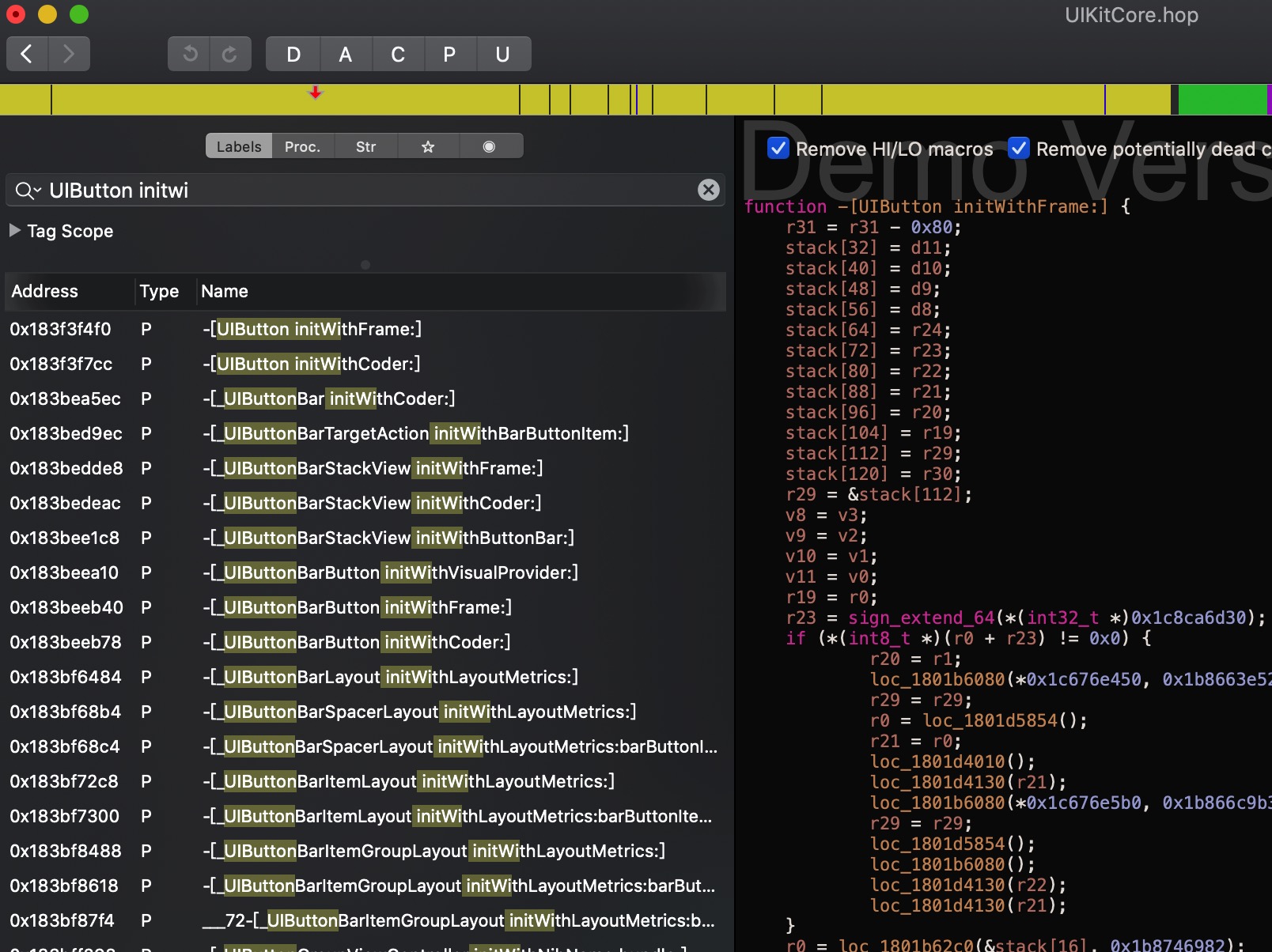
可以通过hopper分析系统库的代码
动态库的加载
在Mac/iOS中,使用/usr/lib/dyld加载动态库,[NSBundle loadBundle]内部也是使用dyld
dyld加载过程可细分为九步:
- 设置运行环境:主要设置运行参数,环境变量,检查进程权限
在Product -> Scheme -> Edit Scheme -> Argument可以配置dyld参数,如:DYLD_PRINT_ENV - 加载共享缓存:也就是
dyld_shared_cache_arm64 - 实例化主程序:读取mach-o文件,加载链接库,segment等信息
- 加载插入的动态库
DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES - 链接主程序
- 链接插入的动态库
- 执行弱符号绑定
- 执行初始化方法。
- 查找入口点并返回。